Zika
There is increasing evidence that supports a link between ZIKA virus infection during pregnancy and adverse pregnancy and birth outcomes, including pregnancy loss, microcephaly, and brain and eye abnormalities. THERE IS NO TREATMENT AVAILABLE FOR A ZIKA AFFECTED PREGNANCY.
ZIKA virus outbreak was identified in Brazil in May 2015, and knowledge about ZIKA virus infection, its potential adverse effects on pregnancy, and transmission is rapidly evolving. As of March 23, 2016, there were 39 countries and U.S. territories reporting active ZIKA virus transmission. Updates on areas with active ZIKA virus transmission are available online at http://wwwnc.cdc.gov/travel/notices.
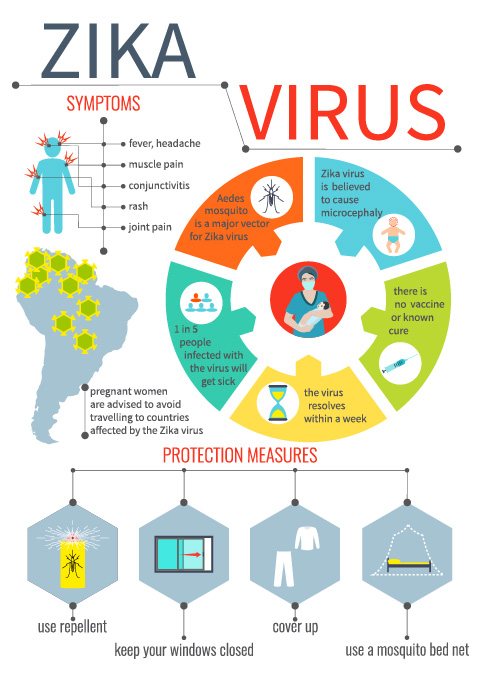
ZIKA virus is primarily transmitted through the bite of infected Aedes species mosquitoes. However, ZIKA virus can also be sexually transmitted from a man infected with the virus to his sexual partners. Based on data from a previous outbreak, most persons infected with ZIKA virus do not show evidence of infection. Signs and symptoms, when present, are typically mild, with the most common being sudden onset of fever, rash, joint pains, and inflammation of the eye.
Women who have contracted the ZIKA virus should wait at least 8 weeks after symptom onset to attempt conception, and men with ZIKA virus disease should wait at least 6 months after symptom onset to attempt conception.
Women and men with possible exposure* to ZIKA virus but without clinical illness consistent with ZIKA virus disease should wait at least 8 weeks after exposure until trying to conceive and if their male partner has a possible exposure they need to wait 6months before trying to conceive. (*Possible exposure to ZIKA virus is defined as travel to or residence in an area of active ZIKA virus transmission, or sex (vaginal intercourse, anal intercourse, or fellatio) without a condom with a man who traveled to or resided in an area of active transmission. )
Women and men who reside in areas of active ZIKA virus transmission should talk with their health care provider about attempting conception. The risk for adverse pregnancy outcomes associated with maternal ZIKA virus infection is currently poorly understood.
IF YOU ARE PREGNANT AND YOUR MALE PARTNER HAS TRAVELLED TO A ZIKA INFECTED AREA YOU SHOULD ABSTAIN FROM INTERCOURSE OR USE CONDOMS FOR 6-MONTHS POST-EXPOSURE.
Let's stay in touch
Our monthly newsletter keeps you up-to-date on healthy lifestyle, latest news, and our practice.



